Economy and society of the aztec empire

The Aztec civilization, known for its highly advanced society filled with unique customs, a comprehensive language, and amazing technology, had a remarkable economy. The economy of the Aztec Empire played a crucial role in its development and success. The Aztec civilization’s history has fascinated and been examined by scholars and enthusiasts globally for many years.
Economy of the aztec empire and the Civilization
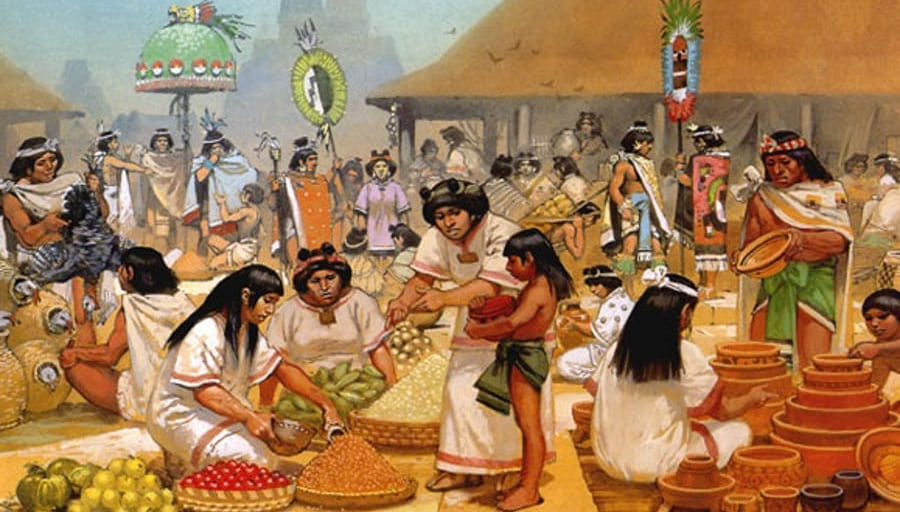
The Aztec economy was very specialized and intricate. The Aztec empire was known for producing an array of items such as tools, pottery, figurines, jewelry, cloth, and baskets. These products were either crafted for the ruler or traded in local markets.



Economic and Cultural Exchange
Some goods were transported to the lowlands of the Gulf Coast, now part of Guatemala, for trade. Among these valuable items were gold ornaments, salt, and finely woven garments. In exchange, the Aztecs received items cherished in their culture, such as jaguar skins, tropical bird feathers, rubber, cotton, chocolate, and cacao beans. These items were essential for various Aztec ceremonies, rituals, and traditions.



Aztec Transportation and Protection
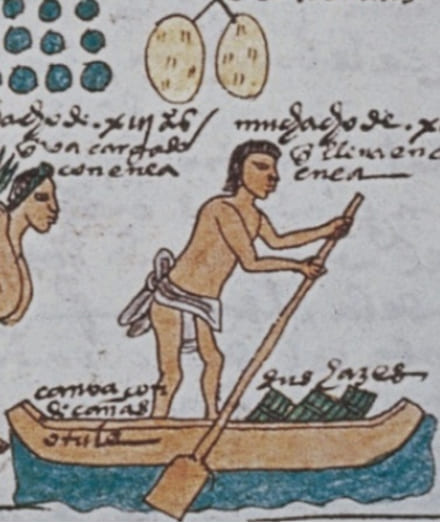
Transporting goods to the lowlands was a significant challenge for the Aztecs. Due to the absence of draft animals and wheeled vehicles, they relied on canoes for moving goods. When water routes were not available, porters carried the items on their backs in long caravans. To protect these caravans in hazardous areas, Aztec warriors accompanied the traders. Additionally, merchants served a dual purpose in Aztec society, acting as spies for the empire in regions not yet conquered by their people.

Language and the Aztec Civilization

The evolution of the Aztec language, Nahuatl, was crucial to their civilization. They used pictographs to depict their written language. Both written and spoken forms of Nahuatl were essential for conducting business transactions and recording family and cultural histories. Additionally, the language was employed to compose beautiful poetry and prose for rituals and ceremonies. Many Aztec traditions depended on their language, which was also vital for transmitting their legends and beliefs across generations.
Significance of Tenochtitlan in Aztec Society

Tenochtitlan, an island city at the heart of the Aztec empire, once boasted a population of approximately 200,000. This city was home to the Great Pyramid, the central site for religious ceremonies and rituals, surrounded by smaller pyramids where incense and sacrificial fires were perpetually lit. The Aztecs’ advanced technology enabled the construction of these impressive step pyramids, some reaching over 100 feet in height. Reflecting the social structure of the civilization, the nobility resided in brick or stone houses, while commoners lived in homes made of interwoven mud and twigs. Tenochtitlan was a vital hub of the Aztec civilization due to its large population and the numerous religious structures and activities that defined its cultural and spiritual life.




Pingback: Did The Aztecs Use Agriculture On Terraces? Find out